You have been given a queue that can store integers as the data. You are required to write a function that reverses the populated queue itself without using any other data structures.
Example:
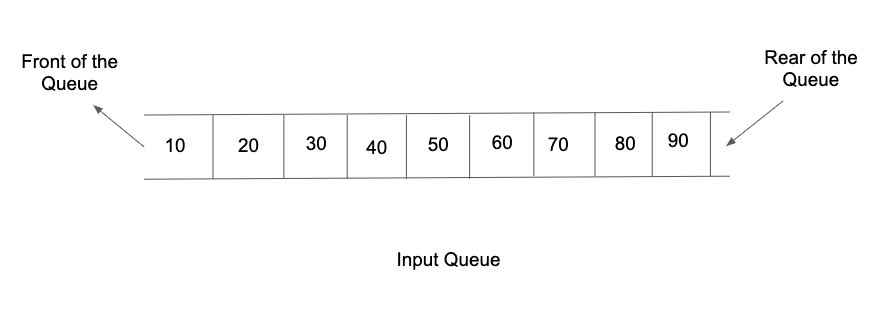
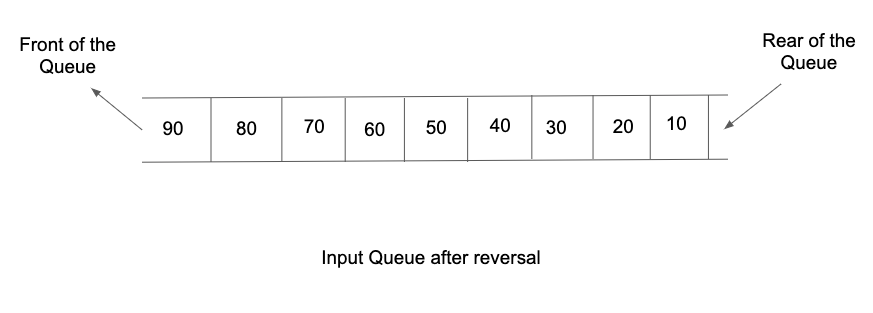
The first list of input contains an integer 't' denoting the number of test cases/queries to be run.
Then the test cases follow.
The first line input for each test case/query contains an integer N, denoting the total number of elements in the queue.
The second line of input contains N integers separated by a single space, representing the order in which the elements are enqueued into the queue.
For each test case/query, the only line of output prints the order in which the queue elements are dequeued, all of them separated by a single space.
Output for every test case/query will be printed on a new line.
Note:
You are not required to print the expected output explicitly, it has already been taken care of. Just make the changes in the input queue itself.
Constraints:
1 <= t <= 100
1 <= N <= 10^4
-2^31 <= data <= 2^31 - 1
Time Limit: 1sec
Sample Input 1:
1
6
1 2 3 4 5 10
Note:
Here, 1 is at the front and 10 is at the rear of the queue.
Sample Output 1:
10 5 4 3 2 1
Sample Input 2:
2
5
2 8 15 1 10
3
10 20 30
Sample Output 2:
10 1 15 8 2
30 20 10
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "solution.h"
int main() {
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
queue<int> q;
int size;
cin >> size;
for (int i = 0, val; i < size; i++) {
cin >> val;
q.push(val);
}
reverseQueue(q);
while (!q.empty()) {
cout << q.front() << " ";
q.pop();
}
cout << "\n";
}
}
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
void reverseQueue(queue<int> &input) {
// Write your code here
if(input.empty())return;
stack<int>st;
while(!input.empty()){
st.push(input.front());
input.pop();
}
while(!st.empty()){
input.push(st.top());
st.pop();
}
}




Comments
Post a Comment